Intellectual property law subjects [Up To Date]
Table of Contents
- What subject is intellectual property?
- Who owns intellectual property?
- Is intellectual property the same as patent law?
- What is the most important type of intellectual property?
- What are the 3 main types of intellectual property?
- What are the 4 types of patents?
- What is an example of intellectual property?
- What skills do IP lawyers Need?
- What type of lawyer makes the most money?
- Where do most IP lawyers work?
- Is copyright a law?
- What is the study of intellectual property law?
- What is patent law?
- What are the 4 types of intellectual property?
- What are the 5 types of intellectual property?
- What do IP lawyers do?
- What are the 7 intellectual property rights?
- Is intellectual property law a good career?
- Are intellectual property lawyers in demand?
- Why is IP law important?
Last updated : Sept 3, 2022
Written by : Enda Maxon |
Current |
Write a comment |
What subject is intellectual property?
Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce.
What is the study of intellectual property law?
Intellectual Property (IP) law relates to the establishment and protection of intellectual creations such as inventions, designs, brands, artwork and music.
What are the 4 types of intellectual property?
Patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets are valuable assets of the company and understanding how they work and how they are created is critical to knowing how to protect them.
What are the 5 types of intellectual property?
- Patents. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office grants property rights to original inventions, from processes to machines.
- Trademarks. Trademarks protect logos, sounds, words, colors, or symbols used by a company to distinguish its service or product.
- Copyrights.
- Trade Secrets.
What do IP lawyers do?
What do IP lawyers do? IP lawyers play a variety of critical roles related to the protection of intellectual property. In some capacities they act as advocates representing clients in court proceedings. They also serve as advisors, counseling clients about intellectual property matters.
What are the 7 intellectual property rights?
Rights. Intellectual property rights include patents, copyright, industrial design rights, trademarks, plant variety rights, trade dress, geographical indications, and in some jurisdictions trade secrets.
Is intellectual property law a good career?
IP law pays well As the global importance of India as a fast-growing market for consumer goods, technology, media, automobiles, and luxury items continue to grow, IP law practice in India will thrive. As law firms continue to compete for talent, salary in IP law practice will remain strong.
Are intellectual property lawyers in demand?
If you're looking for an area of law to specialize in, intellectual property law is a good option because it's a growth area right now. Businesses increasingly run on the strength of their ideas and more money is being made through the sale of concepts and information, rather than the sale of physical products.
Why is IP law important?
Intellectual property protection is critical to fostering innovation. Without protection of ideas, businesses and individuals would not reap the full benefits of their inventions and would focus less on research and development.
Who owns intellectual property?
Generally, the creator of a work is deemed its owner. However, intellectual property ownership can be determined differently for different types of property and under varying circumstances. For example, if work is created for an employer, the employer is the owner of that intellectual property.
Is intellectual property the same as patent law?
"Intellectual Property" is the term used to describe certain categories of rights acquired by businesses to further their business interests. Patent rights are considered intellectual property. It helps in understanding patent rights and their value to compare patents to other forms of intellectual property.
What is the most important type of intellectual property?
Patent. A patent is used to prevent an invention from being created, sold, or used by another party without permission. Patents are the most common type of intellectual property rights that come to people's minds when they think of intellectual property rights protection.
What are the 3 main types of intellectual property?
- Patents. If you have come up with a new invention, you may want to consider protecting it with a patent.
- Trademarks. Let's say that you have come up with a great new name for your brand, company or product.
- Copyrights.
What are the 4 types of patents?
- Utility patent. This is what most people think of when they think about a patent.
- Provisional patent.
- Design patent.
- Plant patent.
What is an example of intellectual property?
Utility patents: for tangible inventions, such as products, machines, devices, and composite materials, as well as new and useful processes. Design patents: the ornamental designs on manufactured products. Plant patents: new varieties of plants.
What skills do IP lawyers Need?
IP attorneys need strong communication skills to talk to clients, judges and other lawyers. Clear communication can help lawyers advise clients and explain legal concepts. If an IP lawyer works in a courtroom, they may also need to develop strong negotiation skills to help them reach legal agreements and settlements.
What type of lawyer makes the most money?
- Medical Lawyers – Average $138,431. Medical lawyers make one of the highest median wages in the legal field.
- Intellectual Property Attorneys – Average $128,913.
- Trial Attorneys – Average $97,158.
- Tax Attorneys – Average $101,204.
- Corporate Lawyers – $116,361.
Where do most IP lawyers work?
Patent lawyers generally work at either law firms in patent or IP law departments, in-house at corporations, for government agencies such as the USPTO, or at universities. Copyrights protect original works of authorship, including literary works, paintings, films, and music.
Is copyright a law?
Copyright is a form of protection grounded in the U.S. Constitution and granted by law for original works of authorship fixed in a tangible medium of expression. Copyright covers both published and unpublished works.
What is patent law?
Patent law is the branch of intellectual property law that deals with new inventions. Traditional patents protect tangible scientific inventions, such as circuit boards, car engines, heating coils, or zippers.

Check these related keywords for more interesting articles :
Trademark law vs copyright law
How much does intellectual property cost
How to search for trademark availability
Can you copyright a song if you dont own the beat
Us trademark renewal timeline
Trademark registration wordmark
What does the us patent and trademark office do
How to get warner brothers copyright permission
Should i trademark first
How to copyright my podcast
What does trademark entail
Intellectual property rights geographical indications
How to trademark a business name in colorado
How to patent an idea worldwide
Do i have to trademark my business name uk
Did you find this article relevant to what you were looking for?
Write a comment
Comment by Jarred Kurkowski
intellectual property law is the new rules for the new economy we've moved from an era when we thought of business assets as things like factories or big physical facilities and now we're turning to an era in which we understand that the real value is created intellectually the products of innovation invention creativity branding these are the sorts of things that are going to create the real value in the modern economy and so we invite you to join us in our specialization on intellectual property law to learn about these new years to learn how patents work copyrights trademarks how intellectual property policy is intended to create the conditions upon which people can invest can create and distribute these new types of value in a modern society you
Thanks for your comment Jarred Kurkowski, have a nice day.
- Enda Maxon, Staff Member
Comment by 3z2r3nH
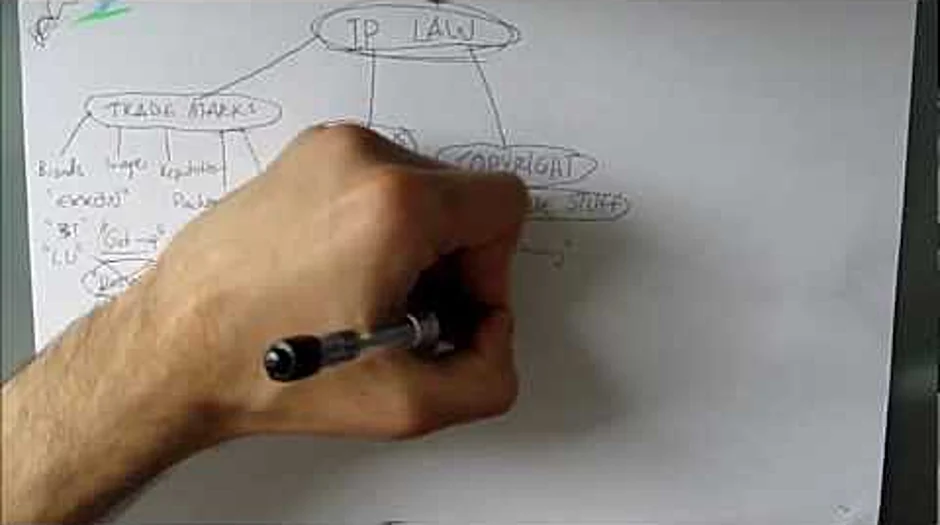
hi everyone and welcome to my first ever tutorial on intellectual property law the reason why I started making these tutorials so simply because I'm now as a student I tried sometimes to youtube videos and how to understand different concepts and I couldn't find anything so I was thinking maybe there are other students like me out there who have the same problem sometimes I will cover the different aspects of intellectual property law the different types of IP law I will cover the cases and the legislation that covers it and further down the line when I'm doing trademarks I will draw some parallels to compare to US law but more than that it's going to be mainly focused on UK law so to jump into it this first tutorial we're just going to look at an Outlook it or-or-or a kind of the framework of how IP love fits together because I think for many people it is important to realize that IP law it's an area where every separate color that you have different separate rights covering different things but they all interrelate to they all kind of overlap in one way or none or another this is very important to understand because when you're actually going into litigation or when you're when you're dealing with clients etc you need to appreciate that they want results but they don't necessarily care about how so just because something is a design from the outset doesn't mean that you cannot try to register it as a trademark to get more protection so they want results and you need to find the results for them the first write that that I will point out is trademarks law or trademarks now my handwriting is very crap so thank you for bearing with me but you have trademarks which is the first right and what are trademarks when you're dealing with trademarks you're dealing with different things you're dealing with brands for instance you're dealing with with the images you're dealing we're dealing with reputation and what I mean with reputation is when you're talking about trademarks trademarks essentially as they act as a guarantor of origin or indicator of origin so it is something that people use to identify who they are where their goods or services come from what they're trying to sell I mean let's take an example you would have Exxon or or BT or you know Louis Vuitton these kinds of things are trademarks usually you will also have packaging under that I will put the rule get up that people usually refer to so if consumers look at that packaging and think oh wait that comes from this certain someone then Paulson potentially you could trademark that as well you could also potentially Praed trademark designs but to avoid confusion just ignore this one for a second and we'll give back to that when we're dealing with trademarks then you also have design rights designs cover things such as the appearance or its ornamentation its design is very self-explanatory and it's it's not a very big area of IP even though it's very widely used I mean very recently you've had the Apple and and Samsung disputes and the disputes that have been going on for quite some time now about the iPad and how Samsung's a tablet looks the same the general gist is a design covers the appearance then you have copyright and copyright is an interesting one because because sometimes people at least in the UK they misunderstand how copyright works or they don't understand quite how it works they think that people have a copyright in everything and anything I mean I had a friend who told me I have a copyright in my name now you do not have a copyright in your name at least in the UK copyright covers let's call it the creative industry things such as music books ie under that will say literary works so anything literary dramatic work so drama and and play sound recordings and what I mean with sound recordings I mean the recorded sound so so if you think about a song a song you would have lyrics as a literary work you will have music the actual melody but then you'll have a separate copyright for everything recorded which may be owned by someone else etc etc if you've ever asked yourself what protection covers computer software well copyright does so I'll write PC so PC programs the coding the actual coding is covered by copyrights patents is the other one you have and patents but it concerns itself with inventions Stan and many people also quite understand how patents work they think you can patent everything and that's also wrong because you can only patent inventions and invent and invention is only an invention when it's new when it is not obvious when it's capable of industrial applications I'm just going to write industrial application and if it is not excluded because you have certain subject matter which under the patent sock have been deemed to be excluded from protection and the biggest area of patents is the pharmaceutical industry but you also have the technology industry and we're thinking about tech you're thinking about something like cell phones more sorry mobile phones computers speakers you've got big companies that usually have thousands of technology patents you've also got a few other rights which fall under intellectual property well for most of you out there you would not even consider them you would not look at them but they're actually one of the era they're actually quite big areas I mean the influence will quite a lot Neville I have a lot of impact on on certain things one is plant breeders rights the other one is semiconductor chips which can also be covered under patents funnily enough if they satisfy the patent requirement what are semiconductor chips well every computer has got a processor and that processor has a semiconductor chip and it is that chip that's protected by this right much so when you're studying IP law you're mainly covering these four areas now the last thing I want to comment is that you potentially have one more right the reason why I'm saying that potentially is because it is it has been and it is still arguable whether this is an intellectual property right now the law of confidence it protects trade secrets that the definition lies in the name the law of confidence so it is it deals with confidential information I will give you an example and that's the coca-cola recipe so you have the law of confidence the problem with this now I'm not going to only write trade secrets I'm also going to write private information but once you start talking about this you're dealing less with commercial IP law and you're dealing more with you know human rights and then the potential right to privacy or privacy whatever you want to call it general know-how not general know-how sorry about that know how the difference between same general know-how and know-how is that general know-how is just general information know-how might refer to that the steps and in doing things whether the way you do things you know the process of doing things within the company an example of this is one know how might be how MacDonnell's they're made how they make their dressing you know how does McDonald's make their burgers tastes the same almost anywhere in the world so th
Thanks 3z2r3nH your participation is very much appreciated
- Enda Maxon
About the author

Enda Maxon
I've studied education policy at Rocky Mountain College of Art and Design in Lakewood and I am an expert in space law. I usually feel surprised. My previous job was model makers, metal and plastic I held this position for 26 years, I love talking about photography and motorcycles. Huge fan of Yung Gravy I practice marathon swimming and collect sports memorabilia.
Try Not to laugh !
Joke resides here...
Tags
Who owns intellectual property
Is intellectual property the same as patent law
What is the most important type of intellectual property
What are the 3 main types of intellectual property
What are the 4 types of patents
What is an example of intellectual property
What skills do IP lawyers Need
What type of lawyer makes the most money
Where do most IP lawyers work
Is copyright a law
What is the study of intellectual property law
What is patent law
What are the 4 types of intellectual property
What are the 5 types of intellectual property
What do IP lawyers do
What are the 7 intellectual property rights
Is intellectual property law a good career
Are intellectual property lawyers in demand
Why is IP law important
 : 5772
: 5772